
PTC versus Thin Film-Based Heaters in BTMS
We all feel the need for extra warmth in cold weather and cooling in hot weather to stay healthy and function effectively. The Li-ion battery cells typically used in today’s commercial electric vehicles (EVs) also need careful thermal management to operate at peak performance and preserve their lifespan.
- Rising temperatures will lead to the reduction of active materials, resulting in a loss of capacity. Meanwhile, internal resistance rises with temperature, contributing to a loss of power output. In the worst case, a thermal runaway can occur, potentially leading to self-ignition and explosion.
- Falling temperatures reduce the efficiency of the chemical reactions within the battery. Therefore, the colder the battery, the lower the capacity and power output. Charging in cold conditions can also damage the battery, reducing its useful life.
It is the role of the Battery Thermal Management System to regulate the temperature within the optimum range for the battery, which is typically 20°C to 45°C, regardless of ambient temperature. In liquid-cooled battery packs, coolant will flow through the battery’s BMS (Battery Management System) to transfer heat to and from the battery cells to the coolant either through direct immersion or conduction through a battery plate or other structure. This coolant from the battery pack outlet port will then flow through the Battery Thermal Management System for conditioning.
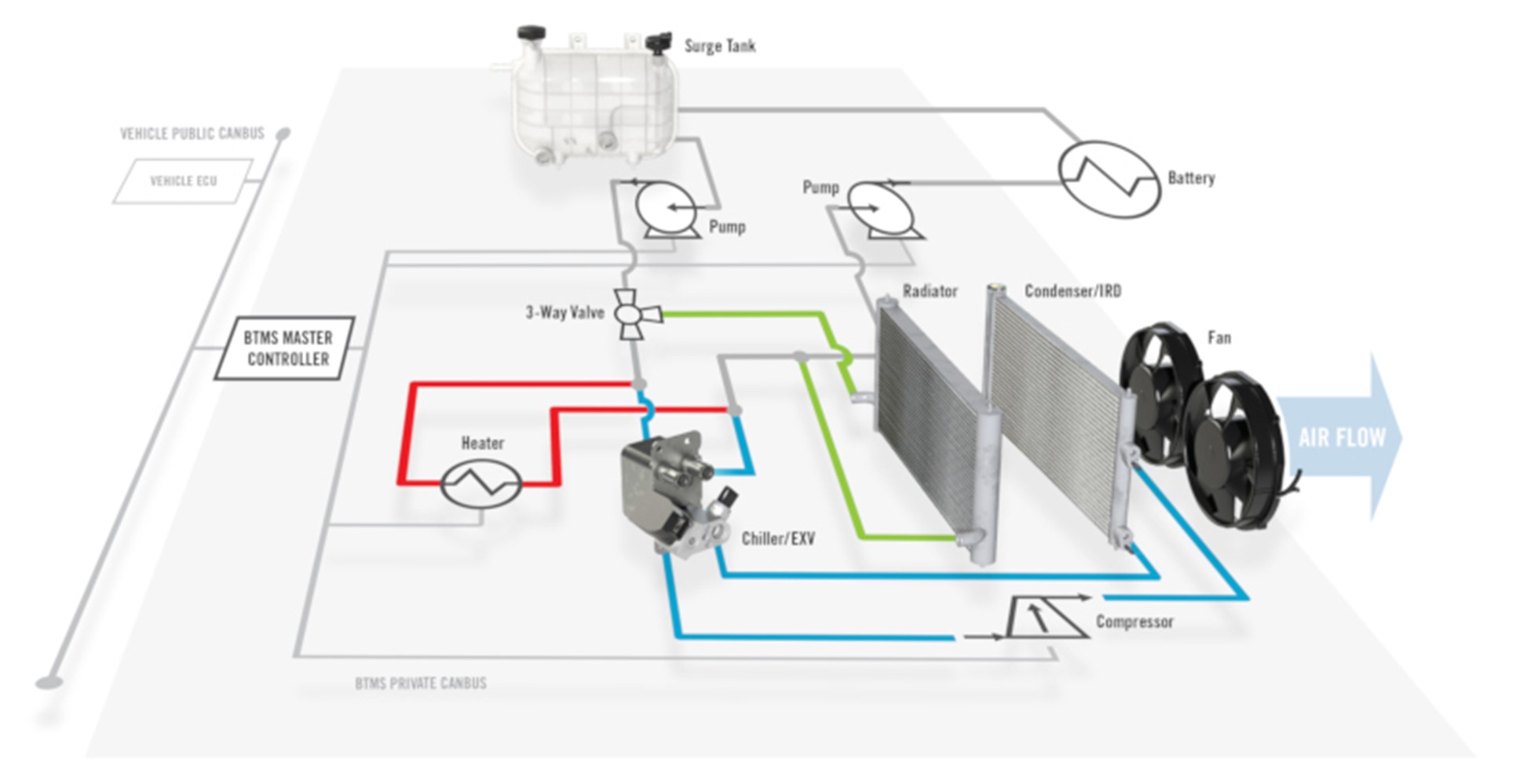
As can be seen in the schematic, one of the key components of the BTMS is the heater, which will heat the coolant and, therefore, in turn, the battery when the battery temperature drops below the minimum threshold. For the high voltages common to commercial EVs, there are two key heater technologies: Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) Heaters and Thin Film-Based Heaters.
PTCs are characterized by a heating element that’s electrical resistance increases significantly with temperature. This rise in resistance reduces the current drawn and thus reduces the power output of the heater. Consequently, this decrease in power dissipation effectively limits the heater’s temperature.
In contrast, Thin Film-Based heating technology, utilized in Modine’s BTMS heaters, comprises a complex layer system of heating elements securely and directly bonded to a heat-exchanging structure that is in contact with the coolant. This design enables nearly loss-free and rapid conversion of electrical power into heat.
Advantages of Thin Film-Based Heaters in the BTMS of Commercial EVs over PTC Heaters are:
- Fast and Precise Heating Adjustment: The intrinsic characteristics of the heating layer of the Thin Film-Based Heater, along with Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control, allow for rapid and precise adjustment of the heat output of the heater, providing more stable operation than possible with PTC heaters and faster heating of the battery pack.
- Higher Efficacy: Thin Film-Based Heaters maintain a constant power output regardless of coolant temperature across a very wide coolant temperature range. Conversely, with PTC technology, power output decreases as soon as the coolant temperature increases. This limits their effectiveness in heating the battery. Additionally, Thin Film-Based Heaters provide the same power output across a wide voltage range, whereas with PTC heaters, any reduction in voltage reduces power output.
- Increased Battery Life: Thin Film-Based Heaters heat up faster than PTC whilst not generating an inrush current when turned on. The lack of any spikes from the inrush current contributes to increased battery lifespan and reduces damage to other electrical components, too.
- Higher Efficiency: As Thin Film-Based Heaters can be controlled seamlessly in small steps (for example, 50W), the energy wastage of the system is reduced.
- Environmental Benefits: Thin Film-Based Heaters are free from rare earth metals and lead, making them more environmentally friendly and supporting robust supply chains.
In summary, Thin Film-Based Heaters offer advantages in terms of fast responsiveness, high levels of control, high efficiency, improved reliability, and environmental considerations when compared to PTC heaters. These characteristics make them an appealing choice, especially for a Commercial EV BTMS.
Modine’s BTMS heaters have operating voltages between 400VDC and 850VDC, delivering up to 10kW of power. In addition, they are IP67 rated, providing assurance around durability in harsh environments. Lastly, they conform to ISO26262 and ISO16750.
As part of the overall BTMS, therefore, the heater plays a critical role. It assures battery life and battery performance during cold weather, demanding a responsive, efficient solution. The Thin Film-Based Heaters that Modine uses are ideal for this, especially when integrated with the other high-performance components in the Modine BTMS. Additionally, the integrated master controller of the BTMS, which includes Modine’s proprietary firmware, ensures that the heater and all other BTMS components work optimally as a system and deliver peak performance to the application. The Modine application engineering team can support determining suitability and product selection based on their varied and extensive experience across a range of commercial EVs.





